Introduction
呢排好忙…都有一段時間無POST過野. 為左令5月唔好空左無POST過, 今日就承接上回講埋Cable Sizing…
Cable Sizing對於電器黎講都算係一個幾大既Topic, 可能呢個Post都未必cover得曬成個Cable Sizing既Concept. 但係我會以一個Consultant角度去講下我平時係會點做Cable Sizing.
首先, 要知道點解要做Cable Sizing先. 好多時候, 做電第一步就係上次咁講, 要畫個Schematic. Schematic既精髓就係Show到曬成個Development要用電既Load係咩位, 個Load大概幾大(睇Protection device rating, 但唔能夠實際反映), Cable幾大同大概走幾長(Schematic剩係睇到Vertically走幾長, Horizontally要睇Layout Plan), Genset房係咩位同大概幾多kVA. 有左呢D information, 基本上你對呢個Development既電Design應該有基本既概念. 所以Schematic好重要, 而Cable Sizing亦都同樣重要, 因爲其實每個Project最貴往往都係Cable, 如果可以充分地Optimize到Cable既Size同長度, 就可以節省好多錢.
Step 1: Current Carrying Capacity
咁睇完上段大家都應該大概估到有咩因素可以影響到個Cable Size, 就係Cable既長度同埋個Load行既Current. 咁好正路, 如果個Load既Current越大 or Cable length越長, 咁條Cable既Size都越大 (或者需要更多Cable). 所以大前提, Cable自己本身要大過個Protective Device既Rating, 而當Cable大過Protective Device既Rating, 自然就會大過埋過Design Current. 所以做Cable Size第一步, 就係要Check個Current Carrying Capacity. Current Carrying Capacity 可以係EMSD 電力守則裏面查到 (Table A6(1) – A6(8)). 下圖為A6(8) (查Multicore XLPE Armoured Cable既表):

呢個表有Show唔同既Ref. Method (其實Voltage Drop某D表都有), 其實EMSD都有圖比大家睇, 去決定用邊個Ref. Method:


所以收銀成日都係用Protective Device去預Cable Size, 其實就係因爲咁.
滿足到上面既條件, 就去到計數比較多既一部份: 就係Volt drop同Copper Loss.
Step 2: Volt Drop
Volt Drop其實就係講緊當電力經Cable由Source到Load傳送既時候, Cable本身有一定既電阻, 所以係電流流過Cable既途中就會產生電壓降, 所以Source同Load就會有輕微既電位差. 如果電壓降太大, 有機會會影響到個Load既Stability. 根據EMSD電力守則2020, 由Source去Load既Voltage Drop係唔可以超過4%. 當然, 唔同Project有唔同要求, 可能有D Equipment比較Sensitive, 所以個Voltage Drop Requirement就再嚴D. (我見過有D Assumption係0.8%)
下一步就係要計個Voltage Drop, 首先我地講左個基本計法先, 之後再講點計 Feeder Cable, 因爲Feeder Cable個Volt Drop其實係等於Submain個Max. Voltage Drop再加自己Feeder Cable本身既Voltage Drop.

係呢條式, Ib就係Diversified Current (A), Z就係Cable既Impedance (mV/A/m), L就係Cable Length(m), 因爲Z個單位係(mV/A/m), 所以要除1000. 之後再除380V (3相, 單相除220V), 就可以計到Voltage Drop個percentage. 至於Z (Cable Impedance)點揾, 係一個好複雜既問題. 首先要去EMSD COP 2020既Table A6(1) – A6(8)睇, 對應唔同Type既Cable同唔同Size既Cable, 有唔同既Voltage Drop數. 由於有太多Table, 我貼左Multicore既XLPE Armoured Cable表比大家做參考 (Feeder Cable最常用):

你會見到, 大過16mm2後有三個數, 分別係R, X 同 Z. R = Resistive Load, X = Inductive Load, Z = Impedance. 如果讀過電既你, 都知道 Z = R + jX, 所以其實用Z呢個數就可以了. 但某D Consultant 講究D的話, 會再睇埋有幾多條Cable同時間一齊走, 考慮埋個Operation temperature, 計埋個Correction factor, 再乘埋個Power factor去揾個Tabulated既Impedance出黎, 但基於太複雜, 我費事講, 同埋呢個方法個數一定係細過EMSD表入面個個Z, 所以最後計出黎個Volt Drop係會再細D. 如果你用EMSD個Z去計, 理論上你個Volt Drop係大過實際既Volt Drop, 所以係日後做Inspection既時候EMSD呀Sir話要度Volt Drop既時候你都知道係會細過你計個個數, 變相有走棧位, 但唔好處係有機會用多左錢, 因爲可能條Cable係可以再細D.
咁呢個計法只係Apply落一條Cable到, 假使你想計Feeder Cable, 而呢條Feeder Cable又可能層層都有Tee off, 咁條Feeder Cable個Voltage Drop係點計? 其實就係將同樣計法計曬所有Submain Cable, 跟住用Excel 揾返Submain裏面最大既Voltage Drop, 然後再加本身Feeder Cable既Voltage Drop, 就係Feeder Cable應有既Voltage Drop.
Step 3: Copper Loss
另一個Requirement就係要Meet到EMSD BEC 2018入面個Copper Loss要求. 咁又講下咩係Copper Loss, 咁Electrical Distribution入面, 難免會有Harmonics or unbalanced phase current, 呢D harmonics同current會產生熱力, 對個Distribution同條Cable自己本身都唔好. 基於Copper Loss係關於Heat, 所以個單位都好自然係 kW.
咁根據BEC 2018, Main Circuit (由中電/港燈隻牛到制櫃個Main ACB) 既Max. Allowable Copper Loss係唔可以大過0.5%, Feeder Cable就唔可以大過1.5%, Submain Cable (L < 100m) 就唔可以大過1.5%, Submain Cable (L >100m) 就唔可以大過2.5%. 最後, Final Circuit (大過32A) 就唔可以大過1%.
Copper Loss個計法就同Voltage Drop有D分別, 但都係Reference翻EMSD COP 2020個Table, 都係Table A6(1) – A6(8), 但今次要睇既就係Cable 既 Current Carrying Capacity. 詳情可以Refer返Step 1.
咁Copper Loss個計法如下:

式裏面既R係Conductor Resistance (查Cable Supplier Data Sheet), T係Ratio of Conductor Operation Temperature to 90 degrees, L 係Cable Length. 計T首先要知道個Conductor既Operating Temperature係幾多, 而去計個Operation Temperature, 可以用下面條式:

Ib 就係 Load既Design Current, Ii就係Conductor Capacity, 呢個數就可以係EMSD既表到查. 至於點解係90-30, 就係因爲EMSD表入面個Ambient Temperature = 30 同 Conductor Operating Temperature = 90. 所以條式入面既Ambient Temperature 都係30.
揾到Operating Temperature後, 就可以計個Ratio of Conductor Operation Temperature to 90 degrees, 可以用以下呢條公式:

有左R, 就可以計到Copper Loss了, 留意翻呢個數個單位係kW, 所以如果要計Copper Loss %, 係要除翻個Active Power Transferred. 咁以三相黎講, 個Power Transferred就可以用以下呢條式:

有左Power, 就可以將Copper Loss除翻Power Transferred再乘100%就係個Copper Loss %了:

記得Voltage Drop個part, 我講過如果計Feeder Cable既時候, 個Voltage Drop就等於Feeder Cable自己既Voltage Drop再加打後Submain Cable既Max. Voltage Drop. 但去到Copper Loss, 個計法就有少少唔同. 個Feeder Cable既總Copper Loss就係等於Feeder既Copper Loss (kW)再加曬所有Submain既Copper Loss (kW), 再除翻個Active Power Transferred. 簡單D, 就係以下呢條式:

根據EMSD, 以Feeder Cable黎講, 呢個數唔可以大過2.5%.
Other Considerations
講左主要兩個Requirement, 但其實做Cable Sizing Calculation仲有其他因素要考慮. 如果Detail d, 其實係會計埋Protective Device on fault時候既Let through energy, 再睇下Cable自己本身承唔記承受到. 當有Fault時, 係Circuit Breaker未成功Isolate到個Fault既時候, 會有Fault Current流過Protective Device再去到條Cable到, 所以其實計Let through energy條式好容易明, 就係下面呢條:

其實就係等於Fault Current既二次方乘返個Circuit Breaker既Operating time. Fault Current就係220V除返個Total Impedance. 個Total Impedance就係條Cable自己本身既Impedance再加Source個個Impedance. 個Let through energy 要細過條Cable可以Withstand到既Energy. Cable Withstand Energy可以Refer下面條式:

S就係個Cable Cross Sectional Area, 就係個Cable Size, 而K係一個Constant, 可以睇一睇Supplier下面呢個表:

Summary
Cable Sizing 個Concept大致上就係咁. 當然, Consultant會將呢個Concept化成Excel, 然後你只要入個Design Current, try下d cable size, 你就有個Result話比你聼條Cable 滿唔滿足到EMSD既要求. 所以我自己都趁有時間寫返呢個教學, 等將來如果我自己用慣左Excel之後, 都可以Revisit翻個Concept. 希望呢篇文可以幫到讀緊書或者做緊野既你. 同埋帶翻個頭盔先, 呢D formula同Concept都係憑我自己做過2間Consultant研究佢地d template, 同埋睇EMSD既教學去寫翻出黎, 所以如果各位資深既電氣佬發現有任何錯, 一定一定要留言指正我, 我都希望自己學到既野無錯~同埋其實呢個Post剩係講左點計, 未講幾時用決定用咩Type既Cable(Busduct/Prefabricated Cable/Armoured Cable…等等), 所以將來有機會會寫埋 🙂
如果覺得個Post有用, 都歡迎Share比你同學仔/同事 🙂

Chung
個Ratio of Conductor Operation Temperature你係唔係要用開氏黎計? 好似係(273+operating temperature)/(273+90)喎。
AC
Nope. 唔打咁多字, 直接cap EMSD個proof比你睇.

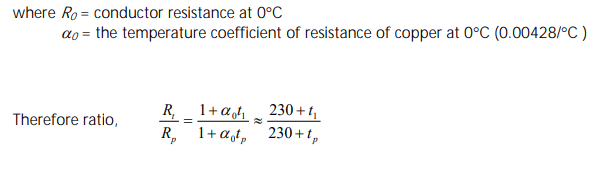
取至EMSD 2005 COP for Energy Efficiency of Electrical Installations Page 27-28
Link
Chung
Thank you, AC.
Kenny
我想問Current Carrying Capacity唔係要用到 EMSD wiring cop入面既 A5 Factors咩?
因為fresh grad岩岩入行 隱約仲記得讀書cable sizing時教過咁既野…
AC
係會用到, 通常都係用A5(1)同A5(3). A5(1)就根據個Cable既Ambient Temperature, A5(3)就係當有好多唔同既Cable同時間走埋一齊既時候就要用到. 因爲呢個Post講簡單例子 (Single circuit, Ambient temperature = 30, 所以全部Factor理論上都係 = 1), 所以無講到A5既Tables.
Kenny
咁第一步sizing既實際做法其實係咪用protective device rated current 同埋A5啲factors 去搵番required minimum Current Carrying Capacity出黎, 之後再對番A6既表去搵番cross sectional area?
AC
係, 可以咁講.
其實係將A5啲factors乘埋曬一齊, 會出一個數 (<=1), 我地叫呢個數做Correction Factor. 之後將個Protective Device Rated Current 除翻個Correction Factor就係個Required Minimum Current Carrying Capacity. 但Cable個Cross Sectional Area就要睇埋Volt Drop同Copper Loss先可以決定到.
David
Ching, 可唔可以時間講埋protective device rated current 同IDMT係點design?
David
Ching, 可唔可以之後有時間講埋protective device rated current 同IDMT係點design?
AC
可以,
IDMT你係想知Time Multiplier同Plug Setting個d?
Protective Device Rated Current -> 你係想知Discrimination點做?
Ken
Hello AC, I remember you posted Circuit Discrimination before but the post seems unable to read now
AC
Don’t seem to remember I have posted about circuit discrimination, can probably talk about it in the future. Thanks!
Ping Kwan Au
你好 AC, 想問問計算電壓降時, 如由三相 submain MCCB 出線 經MCB 箱出單相circuit, 總電壓降應該如何計算? 是否應先計算380V降壓後volt drop, 然後除以Root 3 ,再減去單相circuit 的電壓降, 得出整個circuit 降壓後電壓值?
例如我查表後: sub main circuit 3 相circuit drop 1.5 %, 電壓值是380 x 98.5% = 374.3V
Final circuit 單相circuit drop 2 %, 電壓降是 4.4V
最終電壓值是 374.3V / sqrt 3 -4.4V = 211.7V
總電壓降是 (220V – 211.7V) / 380 = 8.3 V
因本人不確定此算法是否正確, EMSD 亦沒有教3相加單相volt drop 要點計, 希望閣下能在此指點一二。
AC
1. 單相係除220 or 380/sqrt3, 所以你個計法無錯.
2. Three Phase 出Single Phase既總Voltage Drop就係將submain circuit voltage drop % + final circuit voltage drop %. 所以以你個Case黎講, 就係2% (Final Circuit) + 1.5% (Submain Circuit) = 3.5%. 呢個計法係來自IET Electrical Installation Design guide 5.3.3章Summing Voltage Drop 既Example.
3. 根據IET同一個Example, 如果要計出個總Voltage Drop既Value, 個計法就會係: 220 x 3.5% = 7.7V.
我Cap左張圖比你睇:

HK
Hello 師兄, 請問下點解計Copper Loss嘅時候要加晒所有sub-main cables嘅copper loss? 單純理解唔到, thank you
AC
Sorry, miss左你個Reply. 呢個計法係根據IET BS7671裏面既Guideline去計. 至於點解係咁, 我冇去詳細研究.
但你問完呢條問題, 我諗左陣, 再上網睇左睇, 大概都明點解會係咁計.
Volt Drop個概念其實係想計一條Path裏面既電壓降, 而每條Path最大Volt Drop唔可以大過4%. 所以對於每條Feeder打後既Submain Cable, 我地只需要揾最大Volt Drop個條Path就得.
相反, Copper Loss計緊既野其實係Total Power Transferred in Conductors. 姐係對於每條Feeder, 我地都要知道個Total Power Transferred, 所以理論想係要將每條Submain既kW加曬.
KK
A single phase circuit rated at 4kW and cos=0.85 is supplied at 220V 50Hz. It is given that:-
1) The maximum ambient temperature will not exceed 40°C in Summer;
2) It is wired in single-core LSF XLPE (90°C thermosetting) copper conductor cables inside metallic trunking;
3) The circuit is grouped with two other similar circuits in the first 5m of the cable run from the main incoming switchboard, and it will be subject to simultaneous overload.
4) After the first 5m of the run, the cable will be physically separated from the other two circuits and it will be installed on its own inside the metallic conduit mounted on the underside of the ceiling;
5) Before connecting to the load, it was totally embedded within 0.4m length of thermal insulation (fire stops);
6) The total length of the circuit is 35m.
As above situation:
A) What is the minimum size BS88 HRC fuse you will select to protect the circuit?
B) With the voltage drop of the circuit to be restricted at 2.5% maximum, what is the minimum size cable you will select?
C) Whether is the power loss requirement fulfilled for this circuit?
Thanks….
JJ
Ching please help the same question
A single phase circuit rated at 4kW and cos=0.85 is supplied at 220V 50Hz. It is given that:-
1) The maximum ambient temperature will not exceed 40°C in Summer;
2) It is wired in single-core LSF XLPE (90°C thermosetting) copper conductor cables inside metallic trunking;
3) The circuit is grouped with two other similar circuits in the first 5m of the cable run from the main incoming switchboard, and it will be subject to simultaneous overload.
4) After the first 5m of the run, the cable will be physically separated from the other two circuits and it will be installed on its own inside the metallic conduit mounted on the underside of the ceiling;
5) Before connecting to the load, it was totally embedded within 0.4m length of thermal insulation (fire stops);
6) The total length of the circuit is 35m.
As above situation:
A) What is the minimum size BS88 HRC fuse you will select to protect the circuit?
B) With the voltage drop of the circuit to be restricted at 2.5% maximum, what is the minimum size cable you will select?
C) Whether is the power loss requirement fulfilled for this circuit?
thanks
AC
Hi, I assumed is the same question from KK.
You can follow the same procedures stated in this article, the grouping factors should be adjusted to your requirements and use figures for single phase voltage (220V) for the calculation. (https://www.dinhaylo.com/2022/03/10/cable-sizing-example/)
I personally also did the calculation, you can also do it one time yourself to see if our thoughts are aligned.
Based on single phase voltage, Ib(Design Current, after catering harmonics) should be around 21.8A. Hence, 32A fused switch with BS88 HRC fuse should be use. (to
Given your requirements, ambient temperature factor is 0.91, grouping factor shall be 0.87, protective device factor shall be 1, derating factor shall be 0.51. Thus, the total correction factor is 2.47.
By trial and error, I selected 10mm2 1/C XLPE Cu. Cable. With this cable, voltage drop is 1.6%, which is OK.
Using this cable, I also computed the copper loss, which is roughly 0.81%, which is less than 1.5% (Max. Copper Loss for Submain circuit < 100m under BEC), so is OK as well. So 10mm2 1/C XLPE Cu. Cable will be my selection. I believe 6mm2 1/C XLPE Cu. Cable will fail the voltage drop requirement. Feel free to discuss and share your thoughts.
JJ
Thank you so much AC Sir! This is my calculation to share with you ([img]https://upload.cc/i1/2022/10/09/K68ARX.jpg[/img]).
AC
Hi,
Yes, you can use 25A HRC fuses too, I just use 32A switchfuse because it is much more common.
As for Volt Drop and Copper Loss Calculation, I see that you use the switchgear rating instead of the design current for the calculation, which will make the resulting volt drop and copper loss to be slightly bigger.
Also, for copper loss calculation, I usually use Power = I^2R to calculate the copper loss, where R is the conductor resistance and I is the design current. You can refer to the figures from the table of the following link for the resistance values. (Page 19 for single core non-armoured cables) https://www.emsd.gov.hk/filemanager/en/content_725/Guidelines_on_Energy_Efficiency_of_Electrical_Installations_2007.pdf
JJ
BTW, I have another question on fault current calculation, would you please share your solution AC Sir. (https://upload.cc/i1/2022/10/09/8hZ5Vr.jpg) Many Thanks!
Cow Boy
想請教一下Step 3: Copper Loss ge Feeder Cable drop 係咪即係7.4.3 Feeder Circuit drop?
AC
yes, maximum copper loss of feeder cable should not exceed 2.5% according to BEC.